What is dementia?
 Dementia is a category of diseases that affect the brain and person’s cognitive abilities such as thinking and remembering, which can create numerous difficulties in daily activities. It is caused by cell death in the brain. This is a long term condition, which often progressively gets worse as the time passes. About 50-70% of all cases are sufferers of Dementia’s disease, but there are other types of dementia including vascular dementia, lewy body dementia, as well as those that can be caused by other conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, brain infection etc. In cases where dementia occurred due to hypothyroidism, Lyme disease, vitamin B12 deficiency and neurosyphilis, it can be reversible.
Dementia is a category of diseases that affect the brain and person’s cognitive abilities such as thinking and remembering, which can create numerous difficulties in daily activities. It is caused by cell death in the brain. This is a long term condition, which often progressively gets worse as the time passes. About 50-70% of all cases are sufferers of Dementia’s disease, but there are other types of dementia including vascular dementia, lewy body dementia, as well as those that can be caused by other conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, brain infection etc. In cases where dementia occurred due to hypothyroidism, Lyme disease, vitamin B12 deficiency and neurosyphilis, it can be reversible.
This condition has a tendency to be misunderstood by many people who believe it is a natural part of ageing, whilst others think that a simple forgetfulness means dementia. None of these beliefs are accurate. Although dementia mainly targets older population, those above ages of 65 and up, it is not a normal process that happens to everyone who grows old. Around 10% of people will develop dementia at some point and currently it affects more than 36 million individuals worldwide.
What are the symptoms of dementia?
Signs and symptoms of dementia vary from person to person and there are several stages a patient can be diagnosed with, depending on how mild or severe it is.
Cognitive changes may include:
- Memory loss
- Confusion,
- Difficulties with language and communication, finding the right words,
- Difficulties with reasoning, solving problems, dealing with complicated tasks, organising and planning and other similar issues.
In the psychological aspect, it can cause depression, change in personality, anxiety, paranoia, hallucinations etc.
What is the traditional treatment of dementia?
There is no cure for dementia at the moment and aside from providing help to the patient in a form of care and some medications that can slightly improve problems, for most people symptoms deteriorate. However, modern medicine improves daily and new discoveries such as stem cell treatment brought new hope and light to those suffering from this condition.
Dementia as a Consequence of Alzheimer’s Disease
Many cases of dementia can develop both independently and as a complication of Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer syndrome is also caused by the progressive death of brain cells. It often results from a certain combination of genetic, behavioural and environmental factors [2].
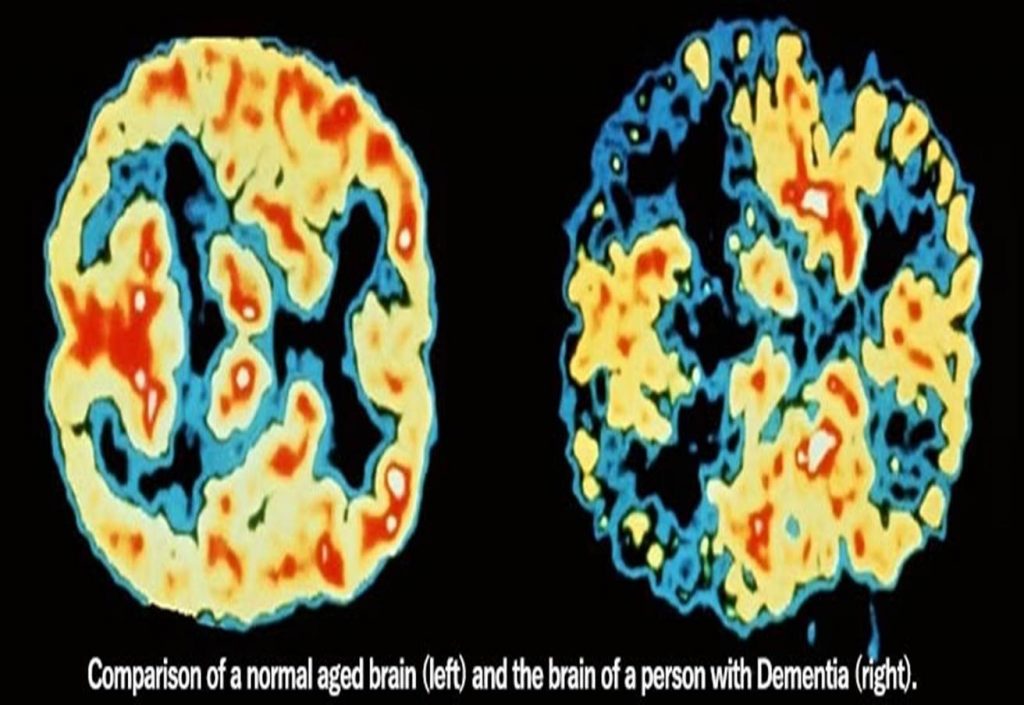
 Pic. 2. Comparison of a normal aged brain (left) and the brain of a person with Dementia’s (right).
Pic. 2. Comparison of a normal aged brain (left) and the brain of a person with Dementia’s (right).
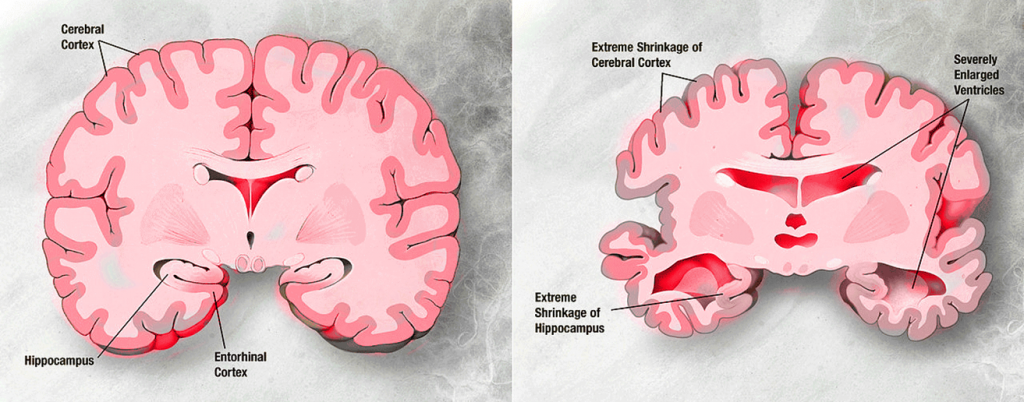
Affected by this disease, the brain loses its cells and connections between them. Along with cells dying, the brain undergoes certain shrinkage. At first, the only symptoms of this process are mild confusion or increasing forgetfulness. However, in time, AD robs a patient of most of the memories. If a person does not undergo a serious Alzheimer therapy, he or she starts suffering from disorientation, speaking and writing problems, social withdrawal, anxiety and depression. Patients suffering from this disease lose their ability to think and reason, make judgements and decisions, plan and perform even simple tasks.
How Regenerative Stem Cells Treatment for Dementia works?
Cell-based therapy aims to restore degenerated neuronal networks, and consequently cognitive function, through the introduction of stem cells. Various scientific research asserts that stem cells make a great contribution to rebuilding damaged nerve fibres. These stem cells may be used as a cellular delivery system, utilising a paracrine “bystander” mechanism through either native or induced production of neuroprotective growth factors. Alternatively, therapeutic restoration may occur through differentiation and participation of the stem cells in repopulating damaged neuronal circuits. This is a finely balanced, complex, and multi step process, with great potential benefit for those suffering from dementia .
A clinical trial showed such therapeutic effects of stem cell transplantation in dementia treatment as:
• increasing acetylcholine levels to improve cognition and memory;
• modulation of neuroplasticity and neurogenesis due to secreting neurotrophic factors by stem cells;
• increasing neuronal survival and neuronal differentiation;
• improving neuropathological and behavioural recovery;
• activation of microglia (glial cells that are located throughout the brain and spinal cord, and act as the first and main form of active immune defence in the central nervous system)
What are the top Benefits of Non-surgical Regenerative Treatments?
With so many options out there, you may be wondering what benefits choosing Non-surgical Regenerative Treatments provides. Over all Regenerative treatments are minimally invasive, non-surgical same day procedures with no risk of rejection, minimal recovery time and minimal worry. You are fully awake and ready to go home within a few hours after injections in the affected area.
Here are the top benefits to be aware of:
